Email Blacklist Monitoring & Remediation: A Developer's Guide
Understanding Email Blacklists
Email blacklists: they're not just a nuisance, they can be a silent killer for your email deliverability. Imagine your carefully crafted messages landing straight in the spam folder, unseen and unread. Let's dive into what email blacklists are and how they work.
An email blacklist is a real-time database of IP addresses and domains known for sending spam or malicious emails. These lists, also known as RBLs (Real-time Blackhole Lists) or DNSBLs (DNS-based Blackhole Lists), are used by Email Service Providers (ESPs) and Internet Service Providers (ISPs) to filter incoming emails. The goal? To protect users from unwanted and harmful content.
Email blacklists come in various forms, each targeting different aspects of email sending behavior.
- IP-Based Blacklists: These lists contain IP addresses associated with sending spam. ISPs use them to block emails originating from these flagged IPs. An example: A healthcare provider might find their appointment reminders blocked if their IP is on such a list.
- Domain-Based Blacklists: These lists track domains known for spam, malicious activities, or poor email practices. If your domain is blacklisted, your sender reputation takes a hit, impacting deliverability. For instance, a small e-commerce store might find all its promotional emails going to spam if its domain is listed.
- Public Blacklists: Maintained by anti-spam organizations like Spamhaus and SpamCop, these open databases list IPs and domains identified as sources of spam.
- Private Blacklists: Email providers maintain internal lists of IPs and domains to block unwanted traffic. These lists are not publicly accessible.
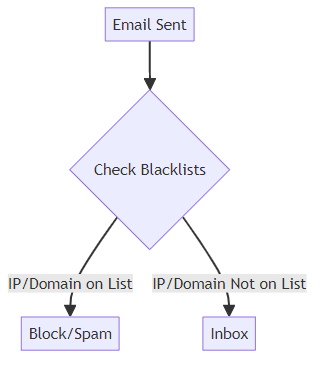
The process of email blacklisting involves several stages:
- Monitoring: ESPs keep a close watch on email activities, tracking volume, bounce rate, and spam complaints.
- Detection: Suspicious behavior, such as hitting spam traps or high bounce rates, damages your sender reputation.
- Listing: If your reputation drops too low, your IP or domain gets added to a blacklist. As TrulyInbox notes, a high spam rate (over 0.1%) or bounce rate (over 0.3%) can land you on a blacklist.
- Checking: Mailbox providers consult blacklists before delivering emails.
- Outcome: Blacklisted emails are either blocked or sent to the spam folder, significantly reducing deliverability.
Understanding these fundamentals is crucial for maintaining a healthy email program. Now, let's look at why domains and IPs get blacklisted.
Why Domains and IPs Get Blacklisted
Are you aware that a single spam complaint can trigger a cascade of deliverability issues? Understanding why your domain or IP gets blacklisted is crucial for maintaining a healthy email program. Let's examine the common pitfalls that lead to blacklisting and how to avoid them.
Several factors can contribute to your domain or IP ending up on a blacklist.
- High spam complaint rates (over 0.1%) significantly damage your sender reputation. If recipients frequently mark your emails as spam, mailbox providers flag your domain as untrustworthy. This can happen if your content is misleading or your audience didn't explicitly opt in.
- Poor-quality email lists lead to high bounce rates and lower trust with email providers. Sending emails to outdated or invalid addresses increases your bounce rate, signaling poor list hygiene. For instance, a retail company using a purchased list might see a surge in bounces and spam complaints.
- Hitting spam traps is a surefire way to get blacklisted. Spam traps are email addresses created solely to identify spammers. Landing in a spam trap indicates that you're not properly vetting your email list.
- A sudden increase in email volume can trigger filters. Sending a significantly larger number of emails than usual can raise suspicion.
- Spammy content and language in your emails also contribute to blacklisting. Using overly promotional language, excessive capitalization, or misleading subject lines can trigger spam filters. Some specific phrases to watch out for include "free money," "act now," "guaranteed," and excessive use of exclamation points.
- Compromised accounts sending unauthorized emails can quickly damage your reputation. If a hacker gains access to your email account and starts sending spam, your IP or domain can be blacklisted.
- Lack of proper email authentication (SPF, DKIM, DMARC) makes it easier for spammers to spoof your domain. Without these authentication methods, mailbox providers can't verify that your emails are legitimately from you.
Using shared IPs for email sending also carries risks.
- Shared IPs can lead to blacklisting if other users on the same IP engage in spammy behavior. If one user sends spam, the entire IP's reputation suffers, affecting all users sharing that IP. Consider the scenario of a small business using a shared hosting provider; if another business on the same server sends unsolicited emails, your email deliverability could suffer.
- Consider using dedicated IPs for critical email sending. A dedicated IP gives you complete control over your sender reputation. This is especially important for transactional emails, such as password resets and order confirmations.
- Monitor the reputation of shared IPs regularly. If you must use a shared IP, use tools to track its reputation and ensure it's not being blacklisted due to the actions of others.
Understanding these factors is the first step in preventing blacklisting. Next, we'll explore how to proactively detect and monitor for blacklisting issues.
Email Blacklist Monitoring: Proactive Detection
Email blacklists can feel like a game of whack-a-mole, but proactive monitoring can keep you ahead of the curve. Detecting blacklisting issues early is vital for maintaining your email deliverability and sender reputation.
Regular monitoring helps you catch problems before they seriously impact your email campaigns.
- Early detection of blacklisting allows for quick action, preventing your emails from consistently landing in spam folders.
- This proactive approach protects your sender reputation, ensuring your messages reach their intended recipients.
- For B2B environments, where reliable email communication is essential for business operations, consistent monitoring is particularly critical, as highlighted by WhoAPI, who emphasizes the importance of seamless communication channels.
For developers, efficient email testing is crucial, and tools like Mail7 can help.
- Mail7 offers a fast and reliable email delivery service, streamlining the testing process.
- With enterprise-grade security and encrypted communications, Mail7 ensures your test data remains protected.
- Mail7's developer-friendly REST API, complete with comprehensive documentation, allows for unlimited test email reception, enabling thorough testing without restrictions.
- Developers can create disposable email addresses, access real-time emails, and automate their email testing workflow, making Mail7 an invaluable tool for email integration and debugging. While not a direct blacklist checker, its robust testing capabilities help ensure your sending infrastructure is sound, indirectly preventing issues that could lead to blacklisting.
Several methods can help you monitor blacklists effectively.
- Manual Checks: Use online blacklist check tools like MXToolbox, MultiRBL, and Spamhaus to manually check your IP address and domain.
- Email Deliverability Monitoring: Track metrics like open rates, bounce rates, and spam complaints to identify potential blacklisting issues. For example, consistently low open rates for a marketing campaign might indicate deliverability problems. You can often find spam complaint data within your email service provider's (ESP) reports.
- ESP Reports: Regularly review reports from your email service provider (e.g., Gmail, Outlook, Mailchimp) for insights into your email performance and any blacklist alerts.
- API Integration: Utilize Email Blacklist APIs for automated monitoring. As WhoAPI explains, these APIs allow you to programmatically check if your email servers are blacklisted, enabling real-time alerts and faster response times.
Staying vigilant about email blacklist monitoring is key to maintaining a healthy and effective email program. Now, let's get into how to remove your IP or domain if it does get listed.
Email Blacklist Remediation: Removing Your IP/Domain
Landing on an email blacklist can feel like a digital dead end, but don't panic! Removing your IP or domain is possible with the right steps.
- Identify the Blacklist: Use tools like MXToolbox or MultiRBL (mentioned in the previous section) to find out which blacklists are causing deliverability issues. Knowing the specific blacklist is the first step to remediation.
- Understand the Reason: Check the blacklist's website for details on why you were listed. Common reasons include spam complaints, hitting spam traps, or compromised accounts. For example, a financial institution might be blacklisted due to a sudden spike in transactional emails after a security breach.
- Fix the Issue: Address the root cause of the blacklisting before requesting removal. Clean up your email list, secure compromised accounts, and improve your email practices.
- Request Delisting: Follow the specific delisting process for each blacklist. This usually involves submitting a request through their website, providing evidence of the steps you've taken to resolve the issue.
- Monitor and Follow Up: Check the removal status regularly and resubmit if necessary. Removal times vary, so be patient and persistent.
Each blacklist has its own unique process for delisting.
- Spamhaus: Requires using their removal portal and providing detailed explanations of the corrective actions taken. Spamhaus Delisting
- SpamCop: Primarily uses time-based automatic removal, meaning your IP will be delisted after a period of no spam activity. SpamCop Reporting
- Barracuda: Provides online delisting tools for a more streamlined removal process. Barracuda Central
- UCEPROTECT: Offers automatic removal after seven days of no spam activity, but also has a controversial paid option for faster removal. As Warmupinbox.com reports, this blacklist targets subnets and entire IP ranges. UCEPROTECT
It's often a good idea to prioritize addressing the blacklists that have the biggest impact on your deliverability. Spamhaus and SpamCop are generally considered highly influential.
What happens if your initial removal request is denied?
- Make additional improvements to your email practices. Focus on reducing spam complaints and improving email authentication.
- Wait a few weeks and resubmit, providing detailed explanations of the steps you've taken. Include documentation and evidence of compliance.
- Consider contacting the blacklist operator directly (if possible) for clarification on why your request was denied and what further steps you can take.
- Remember, patience and persistence are key.
Taking these steps can help you navigate the often complex process of email blacklist remediation. Now, let's talk about how to keep your domain or IP off those lists in the first place.
Preventive Measures: Avoiding Blacklists
Did you know that even with the best intentions, a single misstep can land your emails on a blacklist? Fortunately, there are several preventive measures you can take to avoid this fate.
Here are some key practices to implement:
Maintaining a clean email list is crucial for avoiding blacklists. By regularly cleaning your email lists, you ensure that you're only sending emails to valid and engaged recipients.
- Regularly clean email lists by removing invalid and inactive addresses. This reduces your bounce rate and the likelihood of hitting spam traps. For example, a marketing agency might use email verification tools to remove addresses that haven't engaged in six months.
- Use double opt-in to ensure subscribers genuinely want to receive emails. This practice confirms that the recipient has explicitly agreed to receive your emails.
- Implement a process for handling bounces and unsubscribes promptly. This shows mailbox providers that you're managing your list responsibly. You can track your spam complaint rate through your ESP's reporting dashboard; most ESPs provide detailed metrics on how many recipients marked your emails as spam. Aim to keep this rate consistently below 0.1%.
Email authentication helps verify that your emails are genuinely from you and not a malicious imposter. Proper configuration prevents email spoofing and improves deliverability.
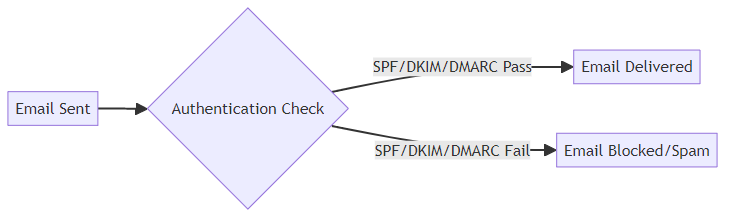
- Set up SPF, DKIM, and DMARC records to authenticate your domain. These records help mailbox providers verify that your emails are legitimate.
- Ensure proper configuration to prevent email spoofing. This protects your domain from being used by spammers.
- Regularly review and update authentication settings. Keeping these settings current ensures ongoing protection.
The content and manner in which you send emails can significantly impact your sender reputation. Adhering to best practices helps avoid triggering spam filters and blacklists.
- Avoid using spammy words and phrases in subject lines and email body. Overly promotional language can trigger spam filters.
- Use mostly text in emails and avoid excessive images. Emails with a high image-to-text ratio are often flagged as spam.
- Add an unsubscribe link in every email. As TrulyInbox notes, this reduces spam complaints and keeps you compliant.
- Keep spam complaint rates below 0.1%. High complaint rates can damage your sender reputation and lead to blacklisting.
By implementing these preventive measures, you can significantly reduce your risk of being blacklisted and maintain a healthy email program. Now, let's look at a specific blacklist that can be a bit tricky.
UCEPROTECTL3 Blacklist: A Special Case
UCEPROTECTL3 is often considered the internet's neighborhood watch, but sometimes the watchman casts too wide a net. Landing on this blacklist can feel like guilt by association, even if your email practices are squeaky clean.
UCEPROTECTL3 targets entire ISPs (Internet Service Providers) or ASNs (Autonomous System Numbers) with a history of abusive behavior. This means that instead of focusing on individual spammers, the blacklist penalizes entire networks.
This blacklist blocks entire IP ranges, affecting innocent senders who share the same network. For example, a small startup using a regional ISP might find its emails blocked due to the actions of other, unrelated clients on that ISP.
While considered legitimate, UCEPROTECTL3 is controversial due to its wide net. Many organizations believe it unfairly impacts legitimate businesses.
UCEPROTECT offers automatic removal after seven days of no spam activity originating from the blacklisted network. This means that if the ISP cleans up its act, your IP range will eventually be delisted.
There is a controversial paid removal option, but it's generally not recommended. As Warmupinbox.com reports, paying for removal might be seen as a "pay-to-play" system and doesn't address the root cause.
Focus on long-term solutions rather than temporary workarounds. Contact your ISP and encourage them to improve their spam filtering and security practices.
Use blacklist monitoring tools to check if you're listed on UCEPROTECTL3. Tools like MXToolbox (mentioned earlier) can help you quickly identify if your IP range is affected.
If problems persist, consider moving to a better host with a stronger reputation for email deliverability. This might involve switching to a different ISP or using a dedicated IP address.
Focus on clean, verified outreach practices to minimize the risk of being flagged as spam. This includes using double opt-in, cleaning your email lists regularly, and avoiding spammy content.
While UCEPROTECTL3 can be frustrating, understanding its scope and focusing on long-term solutions is the best approach. Finally, let's cover some common technical hiccups that can cause blacklisting.
Troubleshooting Common Blacklist Issues
Is your email setup acting strangely? Blacklists might be the culprit, but simple configuration issues often cause deliverability problems. Let's troubleshoot some common technical issues.
- VPNs can sometimes cause blacklisting due to shared IP addresses. If you encounter issues, disable your VPN to see if it resolves the problem. For consistent email sending, consider a dedicated IP VPN.
- Dynamic IPs, often used for residential internet, can be blacklisted more frequently. A static IP provides a more stable and reputable solution.
- Email client configuration problems can also lead to blacklisting. This could include things like:
- Incorrect SMTP server settings: Using the wrong server address or port can cause emails to fail or be flagged.
- Authentication issues: If your client isn't properly authenticating with the SMTP server (e.g., wrong username/password, outdated authentication method), emails might be rejected or marked as suspicious.
- Outdated client software: Older email clients might not support modern security protocols, leading to deliverability problems.
If you still face problems after these checks, move on to more advanced solutions.





